The Federal Budget was delivered this week and classified COVID-19 as the most severe economic crisis in Australia since the Great Depression.
The economic highlights include:
- Real GDP set to fall 3.75% this calendar year, then grow 4.25% in 2021.
- Australian Net Debt estimated to be $703 billion by June 2021 and $966 billion by June 2024.
- Unemployment rate is forecast to peak near 8% in the December quarter and expected to stay above 6% until June 2023.
What the Government is spending in this Budget:
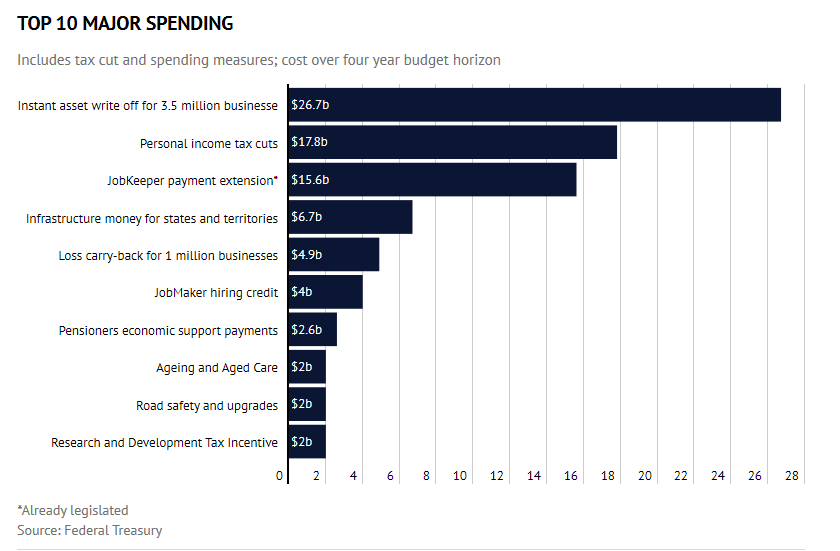
For Businesses
- The instant asset write-off, now referred to as “full expensing”, has been expanded to all businesses with turnover of up to $5 billion until 30 June 2022. This applies to new assets and improvements to existing assets.
- In addition, for small and medium sized businesses (less than $50 million turnover), full expensing is also available for second-hand assets until 30 June 2022.
- Similarly, for businesses with turnover between $50 million and $500 million, full expensing is available for second-hand assets purchased by 31 December 2020 and installed and ready for use by 30 June 2021, capped at $150,000.
- For small businesses (less than $10 million turnover), the balance of the simplified depreciation pool may be expensed in full.
- Temporary loss carry back - corporate tax entities with aggregated turnover of less than $5 billion can apply tax losses from the 2019-20, 2020-21 or 2021-22 income years against previously taxed profits in the 2018-19 or later income years, generating a refundable tax offset in the year in which the losses are incurred.
- Eligible businesses with turnover under $50 million can access the following concessions:
- Immediately deduct certain start-up and prepaid expenditure from 1 July 2020.
- FBT exemption on car parking and multiple work-related portable electronic devices provided to employees from 1 April 2021.
- Access to the simplified trading stock rules from 1 July 2021.
- A two-year amendment period from 1 July 2021.
- Calculate PAYG Instalments based on GDP adjusted notional tax.
- Settle excise duty and excise-equivalent customs duty monthly.
- Access the simplified accounting method for GST purposes.
Encouraging Employment
- Introduction of the JobMaker Hiring Credit for employing eligible young people. Eligible young people are those aged 16-35 who were on JobSeeker, Youth Allowance or Parenting Payment for at least 1 month in the 3 months prior to hiring. In order to access the scheme employers must increase their overall headcount and the newly hired employees must work at least 20 hours per week. The subsidy rates are as follows:
- $200 per week for people aged 16-29
- $100 per week for people aged 30-35
- FBT exemption for retraining and reskilling redundant or soon to be redundant staff. The retraining and reskilling benefits provided may not be related to their current employment.
Source: QHA Bronze Partners – Prosperity Advisers Group.


